In the fast-moving world of medical devices, ensuring safety and effectiveness is paramount. Regulatory bodies worldwide enforce stringent quality management system (QMS) requirements to guarantee consistency, safety, and reliability. These requirements vary depending on the target market and the governing regulations.
ISO 13485:2016 is the globally recognised harmonised standard for QMS in the medical device and in vitro diagnostic (IVD) industries. It is essential for regulatory compliance in regions like the European Union, the United Kingdom, and Canada.
In this article, we explore how ISO 13485 can be effectively implemented to establish a strong and compliant QMS for your business.
Key Elements of ISO 13485
To understand how ISO 13485 helps build a high-performing QMS, let’s break down its core elements:
1. Quality Management System (QMS) Requirements
Organisations must establish, document, implement, and maintain procedures to ensure product quality at every stage of the device lifecycle—from design and development to production, distribution, and post-market surveillance.
2. Documentation and Traceability
Comprehensive documentation ensures regulatory compliance, enhances product accountability, and facilitates efficient problem-solving. All procedures, records, and device information must be properly documented and controlled.
3. Risk Management
ISO 13485 mandates a systematic approach to risk management in line with ISO 14971. This includes identifying, assessing, controlling, and monitoring risks throughout the product lifecycle, with a focus on risk-based decision-making.
4. Design and Development Controls
Manufacturers must implement stringent design and development processes, including verifying and validating product designs and maintaining full traceability of design changes.
5. Supplier Management
A robust supplier management system is essential. Companies must evaluate, monitor, and manage suppliers to ensure the quality of purchased components and services.
6. Internal Audits
Regular internal audits assess the effectiveness of the QMS, ensuring ongoing compliance, identifying non-conformities, and highlighting areas for improvement.
7. Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA)
Organisations must establish processes to identify nonconformities, investigate their causes, and implement corrective actions. Preventive actions should also be taken to mitigate potential risks before they occur.
Why is ISO 13485 Important?
ISO 13485 is more than a regulatory requirement—it’s a strategic framework for quality excellence. Here’s why it matters:
1. Global Market Access
ISO 13485 certification is mandatory in key markets such as the EU and the UK. Compliance simplifies regulatory approval and facilitates international trade.
2. Enhanced Customer Trust
Certification demonstrates a commitment to quality and patient safety, fostering trust with customers, healthcare professionals, and regulatory authorities.
3. Regulatory Compliance
ISO 13485 is a globally harmonised standard. Many regulators, including the FDA, reference it within their frameworks. A compliant QMS ensures alignment with multiple regulatory requirements.
How to Build a Robust ISO 13485 QMS
Implementing ISO 13485 effectively requires a structured approach. Here’s a roadmap for success:
1. Conduct a Gap Analysis
Evaluate your current QMS against ISO 13485 requirements to identify gaps. This analysis informs resource allocation and process development. If no QMS exists, start from scratch with expert guidance.
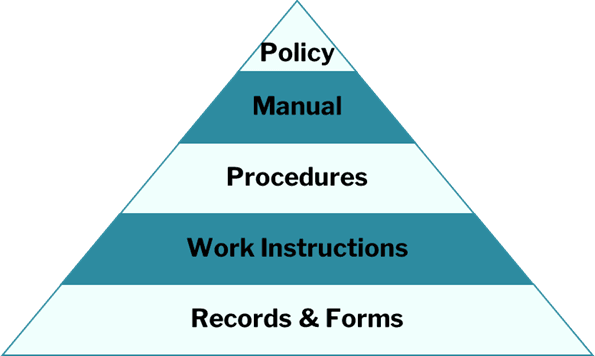
2. Develop a Quality Manual
A quality manual outlines your company’s policies, objectives, and QMS processes. For more guidance, see our article: ISO 13485 Quality Management System Implementation: A Guide to Creating a Quality Manual.
3. Establish Regulatory-Specific Procedures
Depending on your target market, specific procedures must be implemented:
- Risk Management – Develop systematic risk assessment processes in line with ISO 14971:2019.
- Clinical/Performance Evaluation – Establish evidence-based processes to ensure ongoing safety and effectiveness.
- Post-Market Surveillance (PMS) – Define PMS procedures tailored to your device’s risk classification.
- Post-Market Follow-Up (PMCF/PMF) – Implement continuous monitoring systems for real-world performance assessment.
- Vigilance Reporting – Create protocols for managing adverse events and product recalls efficiently.
4. Implement Design Controls
Ensure robust design and development controls, covering design inputs, outputs, verification, validation, and risk mitigation. Early implementation prevents certification delays and costly remediations.
See ‘What Are the Main Phases of Medical Device Development: Do you Understand the Requirements?’ for more information on design requirements.
5. Get Certified
Once your QMS meets ISO 13485 requirements, undergo an audit by an accredited certification body. Certification demonstrates compliance and enhances credibility.
6. Set Up Supplier Management Protocols
Develop a system for evaluating, selecting, and monitoring suppliers to maintain product quality.
7. Train Employees
ISO 13485 compliance requires ongoing staff training. Interactive training sessions and open discussions enhance understanding and engagement.
8. Conduct Internal Audits and Drive Continuous Improvement
Regular audits identify areas for enhancement. ISO 13485 is rooted in continuous improvement, ensuring sustained compliance and operational excellence.
Final Thoughts
ISO 13485 is the foundation of a compliant and high-performing QMS in the medical device and IVD industry. Beyond regulatory compliance, it ensures product safety, risk management, and continuous quality improvement. Embedding ISO 13485 in your organisation paves the way for long-term success in a competitive, highly regulated industry.
Need further help?
If you have any questions or need help with your quality management system, or need help to create, implement or remediate your QMS, please get in touch with our expert consultants today, by phone on +441484662575 or via email at info@lfhregulatory.co.uk.
FAQ’s for ISO 13485
What is ISO 13485?
ISO 13485:2016 is the internationally recognised standard for quality management systems (QMS) in the medical device and in vitro diagnostic (IVD) industries.
Why is ISO 13485 important for medical device manufacturers?
It ensures consistent product quality, patient safety, and regulatory compliance. Certification also provides access to key markets such as the EU, UK, and Canada.
Is ISO 13485 mandatory?
Yes, in many markets. It is required for CE Marking in Europe and is referenced by regulators worldwide, making it essential for global market access.
What are the key elements of ISO 13485?
Core elements include risk management, design and development controls, supplier management, documentation and traceability, internal audits, and CAPA processes.
How does ISO 13485 relate to ISO 14971?
ISO 13485 requires manufacturers to implement risk management in line with ISO 14971, ensuring product risks are identified, evaluated, controlled, and monitored throughout the lifecycle.
How do I implement ISO 13485 in my organisation?
Start with a gap analysis, develop a quality manual, implement regulatory-specific procedures, establish design controls, train staff, and set up supplier management protocols.
How long does ISO 13485 certification take?
The timeline varies depending on the maturity of your QMS. New systems may take 6–12 months to implement before undergoing certification audits.
What is the role of internal audits in ISO 13485?
Internal audits ensure your QMS remains effective, compliant, and continuously improving. They help identify non-conformities and prepare you for external audits.
What happens if my QMS does not comply with ISO 13485?
Non-compliance can lead to certification failure, regulatory penalties, market access delays, and potential safety risks.
Can consultants help with ISO 13485 compliance?
Yes. Specialists, like LFH Regulatory, can support with creating, implementing, or remediating your QMS, ensuring it meets ISO 13485 requirements and is audit-ready.
- Laura Friedl-Hirst
- Laura Friedl-Hirst
- Laura Friedl-Hirst
- Laura Friedl-Hirst
- Laura Friedl-Hirst
- Laura Friedl-Hirst
- Laura Friedl-Hirst
- Laura Friedl-Hirst
- Laura Friedl-Hirst
- Laura Friedl-Hirst
- Laura Friedl-Hirst
- Laura Friedl-Hirst
- Laura Friedl-Hirst
- Laura Friedl-Hirst
- Laura Friedl-Hirst
- Laura Friedl-Hirst
- Laura Friedl-Hirst
- Laura Friedl-Hirst
- Laura Friedl-Hirst
- Laura Friedl-Hirst
- Laura Friedl-Hirst