Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) is quickly revolutionising healthcare globally by enabling innovative solutions for diagnosis, treatment, and patient management. Whilst these amazing developments are being made, risk management is critical to ensuring patient safety and compliance with standards (such as ISO 14971) and regulations (such as MDR (EU) 2017/745). It’s critical to have a well based understanding to effectively manage risks, avoid lapses in compliance and mitigate any harm to patients. In this blog, we’ll explore the importance of robust risk practices and delve into some actionable strategies to manage risk in SaMD development to ensure you always stay on the right path.
What is Risk and Risk Management?
According to ISO 14971, risk is defined as:
“The combination of the probability of occurrence of harm and the severity of that harm.”
Effective SaMD risk management is the systematic application of policies, procedures, and practices to analyse, evaluate, control, and monitor risks throughout a product’s lifecycle. It forms the foundation of any compliant medical device software process.
Building a Risk Management Framework for SaMD
Implementing a structured risk management framework is the cornerstone of SaMD risk management. Adhering to ISO 14971 ensures that you:
● Identify hazards early
● Evaluate and prioritise risks
● Apply appropriate control measures
● Monitor effectiveness continuously
A well-defined approach supports lifecycle compliance and ensures that risk management isn’t a one-off activity but a living system that evolves with the product and is integrated into your QMS.
At LFH Regulatory, we offer tailored QMS template packages including up to 4 hours of support with our consultants. Click here to view our packages and enquire today.
The below core principles of risk management should be taken into account in order to create the robust framework:

Cybersecurity as a Compliance Priority
One of the most critical elements of SaMD risk management is cybersecurity. SaMDs are especially vulnerable to cybersecurity threats, which can impact device functionality, patient safety and data protection. Regulatory bodies now put emphasis on cybersecurity as a critical component of compliance and expect cybersecurity to be embedded into the design and risk framework from the beginning. ISO 27001 and MDCG 2019-61 gives some good guidance on cybersecurity for medical devices, alongside ISO 14971 and IEC 62304.
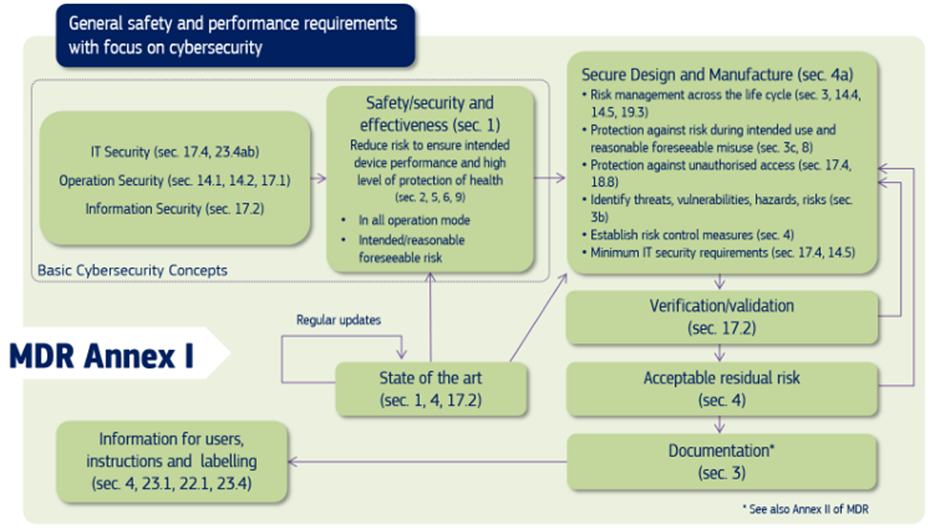
The below diagram shares cybersecurity requirements contained in MDR Annex I – MDCG 2019-61
Integrating IEC 62304 with ISO 14971 for Software Risk
IEC 62304 outlines the lifecycle processes for medical device software.
This standard has helpful information on the software safety classification, development lifecycle processes, validation and maintenance of your SaMD.
When integrated with ISO 14971, it strengthens your SaMD risk management approach by tying risk controls directly to software design, verification, and maintenance processes to ensure risks are appropriately mitigated.
It’s critical to remember that IEC 6230 and ISO 14971 are not two separate processes, they go hand in hand and integrate at almost every step. When software changes, the risk must be reviewed and updated if needed, appropriately verified, and the risks mitigated as far as possible.
Check our SaMD services here
Establishing Post-Market Surveillance for SaMD
Risk management doesn’t end when your SaMD is on the market; it is live for the lifecycle of the software, with PMS cycling back to the risk management system. It ensures that your risk controls remain effective in real-world use and helps capture new or evolving safety issues that weren’t identified during development.
The best PMS strategies:
- directly feed into the risk file
- feedback and incidents continuously inputting back into the risk system
- provides information and evidence on the effectiveness of risk control
- ensures that risk control measures are working as intended
- identifies areas for improvement
Team Training and Regulatory Intelligence
Keeping your team trained and your regulatory intelligence current is a key component of SaMD risk management. Without updated knowledge of standards like ISO 14971, IEC 62304, and BS/AAMI 34971:2023, your risk processes can become outdated, increasing your exposure to compliance gaps.
Check out our Regulatory Intelligence services here.
Risk Management for SaMD with Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence introduces additional complexity into SaMD risk management.
There are additional risks presented by AI or ML (Machine Learning), such as
- Bias – Data input to train the device needs to be free from biases.
- Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment –There needs to be controlled training of the code, validation, verification and release.
- User workload – The AI system needs to be tested to make sure it can handle the workload.
Use of standards like BS/AAMI 34971:2023, which builds on ISO 14971 to cover AI-specific risks, helps you stay compliant and avoid introducing bias, uncontrolled learning, or performance gaps in your product.
Consequences of Inadequate Risk Management
Failing to implement proper risk management activities can have serious consequences:
Increased safety issues both general and towards the patient:
Software malfunctions or cybersecurity breaches could harm patients or compromise sensitive data.
Regulatory Non-Compliance:
Lack of adherence to standards like ISO 14971 can lead to delays in approvals, fines or even product recalls.
A regulatory intelligence system that does not capture relevant and applicable updates will set up the SaMD for failure, as this will mean your SaMD complies to now obsolete guidance, increasing the risk.
Reputational Damage:
Safety incidents can erode trust in your brand, impacting customer loyalty and market share.
Legal liability:
Manufacturers may face lawsuits if inadequate risk management leads to patient harm.
Best Practice Recommendations for SaMD Risk Management
✅ Be proactive; integrate risk controls early and across the lifecycle
✅ Follow standards such as ISO 14971 and IEC 62304
✅ Conduct routine risk reviews and PMS
✅ Train your team and track regulatory changes
✅ Embed cybersecurity into the risk framework
Conclusion
Managing risk in SaMD isn’t solely about avoiding costly compliance mistake, it’s about ensuring patient safety and building trust in your product. For SaMD, where risks can be complex and evolving, a robust risk management strategy is essential. By adhering to core principles, leveraging best practices, and staying vigilant, manufactures can mitigate risks, comply with regulations and deliver safe and effective products to market.
Need Support?
Our expert medical device regulatory consultants can help you build and maintain an effective SaMD risk management strategy. Whether you’re launching a new product or updating an existing one, we can ensure you’re compliant, secure, and audit-ready. Contact us today to see how we can help.
FAQ’s for Managing Risk in SaMD
What does risk management mean in SaMD?
In Software as a Medical Device (SaMD), risk management means identifying, controlling, and monitoring risks throughout the software lifecycle. It follows ISO 14971, which defines risk as the chance of harm combined with how severe it could be.
Why do I need a risk management framework for SaMD?
A risk management framework helps you spot hazards early, control them effectively, and prove compliance with ISO 14971. It also keeps risk management active inside your quality management system (QMS).
How important is cybersecurity in SaMD risk management?
Cybersecurity is essential in SaMD because software is vulnerable to hacking and data breaches. Regulations expect you to build cybersecurity into your design using standards like ISO 27001, ISO 14971, and IEC 62304.
What’s the difference between ISO 14971 and IEC 62304 for SaMD?
ISO 14971 is the standard for medical device risk management, while IEC 62304 is the standard for medical device software lifecycle processes. Together they ensure risks are controlled during design, testing, release, and updates.
Why is post-market surveillance important in SaMD risk management?
Post-market surveillance collects real-world safety data to check if your risk controls work. It also helps you find new risks and keep your software safe and compliant over time.
How does artificial intelligence affect SaMD risk management?
AI adds extra risks like biased data, unpredictable behaviour, and learning errors. Following standards such as BS/AAMI 34971:2023 helps manage these challenges and keep AI-based SaMD safe.
What happens if SaMD risk management is not done properly?
Poor SaMD risk management can lead to safety issues for patients, failed compliance, reputational damage, legal problems, and even costly product recalls.
What are best practices for SaMD risk management?
Best practices include starting risk management early, embedding cybersecurity, aligning with ISO 14971 and IEC 62304, running regular reviews, keeping staff trained, and updating processes as regulations change.
Amrita Bansal
Amrita supports with Quality and Regulatory knowledge for medical devices throughout the
product lifecycle, helping to get innovative devices on the market for patients. She also helps
with overseeing the Regulatory Intelligence efforts, including impact assessment and global
regulatory surveillance.
Amrita has a background in product registrations, medical information, product technical
complaints for pharmaceuticals and combination products before transitioning to regulatory
affairs where she has continued to build up her expertise. Amrita has helped numerous
clients with different portions of their regulatory journeys, from a full QMS implementation, to
usability, to technical file creation, to regulatory strategy and classification.
Amrita is driven by a passion for patient safety, having seen first-hand real-world impacts of
bringing safe and reliable products to market. She combines her knowledge with her
practical expertise to ensure that she can deliver strategic but compliant approaches for her
clients and their medical devices/ technologies.




